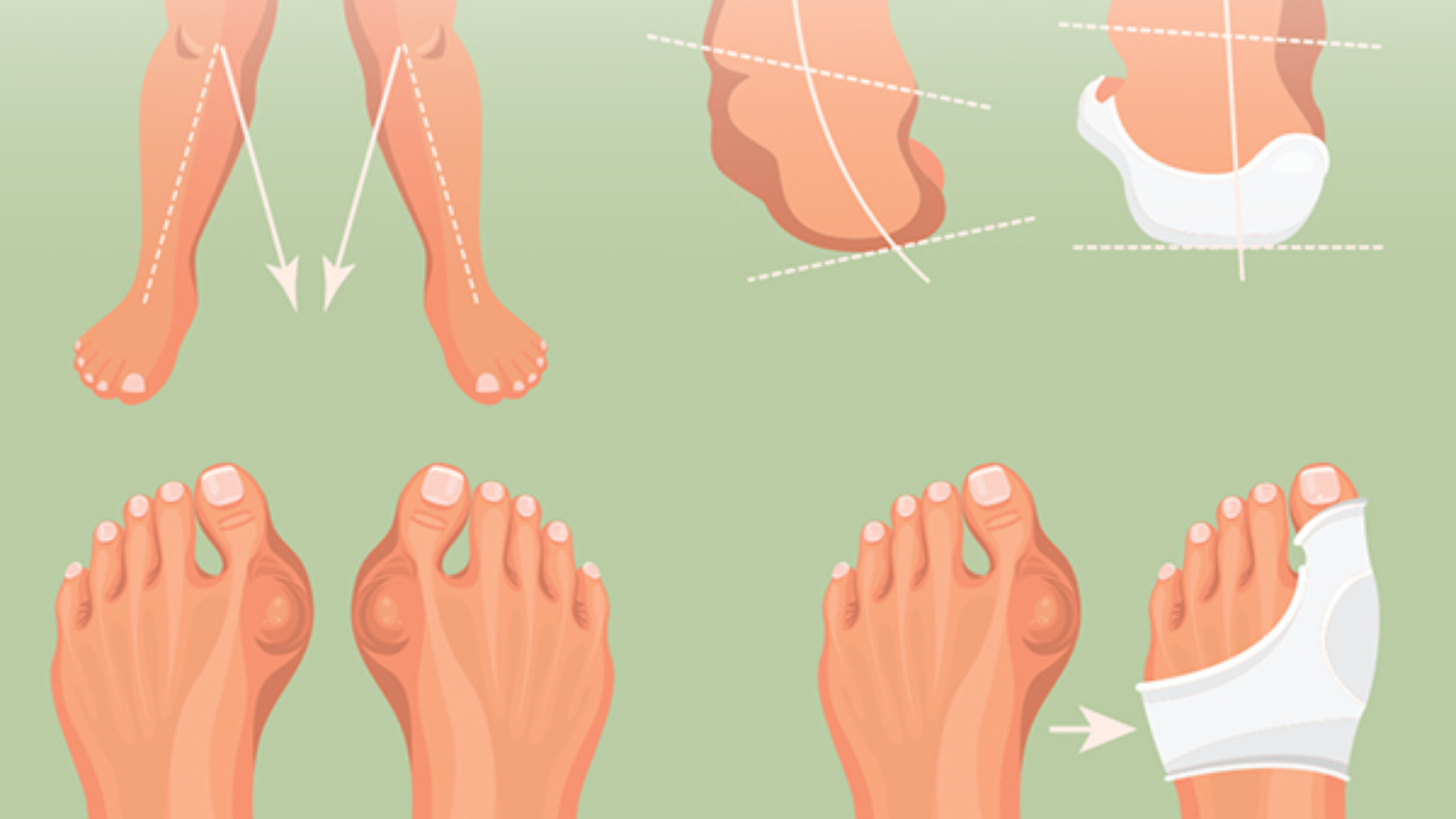
A bunion also referred to as hallux valgus, is a prominent and painful bump that forms on the foot inside in the joint of the large toe. They develop gradually and are quite common in the adult population. The big toe usually bends towards the other toes causing the joint connecting it to the foot to become red and painful.
Over time, the bone structure is altered and a bunion bump develops. This condition may have complications including arthritis or bursitis if left unchecked. The symptoms tend to appear at later stages and may be absent in some people. Bunions are more common in women than in men, as women tend to wear narrow and tight shoes that squeeze the toes together.
The Causes of Bunions
While the exact cause of bunions is unclear, it is often the result of heredity. Some individuals inherit feet with a defective mechanical structure that makes them prone to developing bunions.
Wearing ill-fitting shoes, particularly shoes with narrow and pointed toe boxes or high-heeled shoes may force the toes into the unnatural position. Having an inflammatory condition like rheumatoid arthritis or neuromuscular conditions like polio can also lead to bunion formation.
Bunion Progression
Foot bunions start out small and tend to worsen over time especially if you continue wearing tight, narrow shoes. Since the largest joint in the big toe flexes with each step, it becomes more painful and difficult to walk as the bunion gets bigger. An advanced bunion will alter the appearance of your foot significantly. Not all cases of bunions are similar. Some progress much faster than others.
In severe cases, the big toe can angle all the way over or under the second toe. Sometimes, calluses may form where the toes rub against one another resulting in difficulties walking and additional discomfort. A bunionette (tailorâs bunion) is another type of toe bunion that develops on the base of the small toe. It is very much like a bunion even though it forms in a different location.
Symptoms
In addition to the prominent bump on the foot, the symptoms of bunions include:
· Pain and tenderness
· Inflammation and redness
· Calluses or corns on the bump
· Restricted motion and stiffness in the big toe
· Difficulty walking
Diagnosis
A foot and ankle surgeon will be able to diagnose your bunion from the appearance of your toe and your symptoms. Nonetheless, the surgeon may order X-rays. X-rays provide a clear image of your bone structure and will allow the surgeon to check your toe alignments and inspect the damage to the big toe joints.
Your foot bone alignments change when you sit or stand. X-rays are taken while you are standing to determine the extent of misalignment. The Surgeon will determine the severity of the bunion and develop a suitable plan to correct it.
Bunion Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatment
In many cases, you can treat bunions without surgery although these options cannot “reverse” the condition. They help manage the pain and stop them from worsening.
· Footwear changes – In most cases, bunion pain can be managed by simply switching to well-fitting shoes that don’t compress the toes. Frederick Foot and Ankle can provide information on proper shoe fit and the shoe types that are best for you.
· Padding – Protective pads will help cushion the painful areas around the bunions. You can obtain these from your podiatrist surgeon, pharmacy or drugstore.
· Orthotic Devices – Your foot and ankle surgeon may prescribe custom orthotic devices. These devices take the pressure off the bunion. They may include toe spacers and night splints among others.
· Modifying Activities – In some cases, avoiding or reducing activities that cause pain such as standing for long periods provides relief.
· Ice – Ice application for about 20 minutes several times a day helps reduce swelling
· Medication – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as naproxen and ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and swelling
· Corticosteroid Injections – Corticosteroid injections are rarely used to treat bunions but may be beneficial in reducing inflammation around the bunion.
Surgical Treatment
Your foot and ankle surgeon may recommend bunion surgery if the symptoms do not improve after footwear changes and non-surgical treatments. Surgery realigns your bones, tendons, and ligaments to bring your big toe back to its natural position.
Several surgical procedures are available to rectify bunions including bunion removal (exostectomy), joint realignment (osteotomy) and joint surface removal (arthrodesis). At Frederick Foot and Ankle, we will select the appropriate procedure based on the severity of the deformity, age, activity level, and other factors.
Feel free to contact Frederick Foot and Ankle if you exhibit any of the symptoms associated with bunions for diagnosis and treatment. Remember, the earlier intervention can prevent the condition from worsening.

Add a Comment